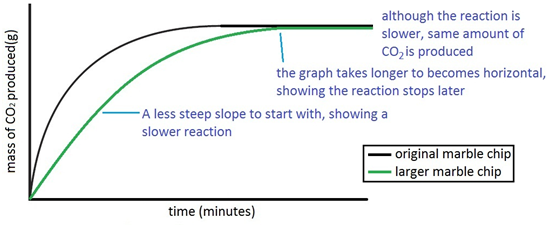
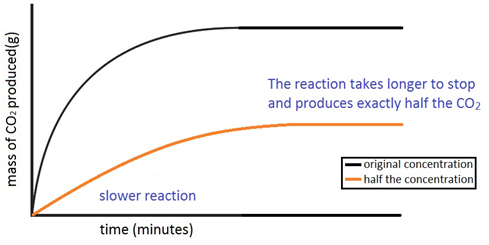
In this experiment i am going to see if temperature affects the reaction rate between marble chips and hydrochloric acid by timing the release of carbon dioxide in the reaction.
Marble temperature effects.
When you stand on wood flooring or carpet the fibers and tiny air.
To this end one control and three different types of mixes are prepared and exposed to high temperature with 300oc 600oc and 900oc for one hour at.
The heat will then dissipate through the marble quickly so the marble doesn t feel any warmer.
The test results show that there are multiple splitting surfaces along the axial direction of marble after high temperatures and the split failure mode is the main destructive manner of marble.
In this study the effects of high temperatures on physical on mechanical properties of self compacting lightweight concretes with marble powder are investigated.
This is due to the kinetic theory.
In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened surfaces removal of material and loss of carved details.
The forces of nature may produce a decaying effect on the look and structural reliability of marble.
Stone surface material may be lost all over or only in spots that are more reactive.
If the marble has any impurities which is likely other minerals may have other reactions at different temperatures.
Rain water particularly in.
Marble is a very dense hard stone and this makes it easier for heat to transfer from a warmer object such as the soles of your feet.
You may consider applying a sealer to the top surface only of a table or countertop allowing the bottom surface to breath well to keep rainwater standing on the surface from absorbing which will eliminate the major cause of cracking etc.
Marble is a dense rock and with no water absorption capabilities cold air shouldn t bother it.
These agents include temperature snow rain wind and atmospheric pollutants.
The reason that marble feels cold is because it conducts heat differently than other surfaces.
The more heat that is given to matter the faster the particles.
Your burner should ideally never allow the marble to reach 1500 c.
I predict the higher the temperature the faster the reaction rate.
Weathering agents normally act in combination with the other agents to increase the deterioration of marble.
When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air and rain react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves.
Weather effects on marble.
Concrete will absorb water and crack at this temperature.
Pure marble being caco3 at standard atmospheric pressure will convert to lime cao and give off co2 at about 1500 c.